
Lighting is a very aspect of any building. Hotel being a ‘home away from home’, lighting plays an important role in the comfort and safety of the occupants of the building.
DAY LIGHT: Day light is an important factor in appearance of a room,so much, so that no décor should take place without taking into consideration the amount of day light that enters a room. Curtains can also be used to control the amount of light that enters a room.
ARTIFICIAL LIGHT: This light is used to substitute or in association with day light. It can be used to contrast or emphasis certain areas by highlighting certain areas. It can also produce harmonious effect throughout the room.
IMPORTANCE OF LIGHTING.
A good lighting design is realized if –
- All spaces (entry, transition, linger, work, and exit) are properly composed in a clear hierarchy of importance and purpose.
- Make it possible to see quickly without strain.
- The lighting mood is consistent with the function and design of each space and is pleasing to the eye.
- It promotes productivity.
- Eliminates hazards.
- It is readily maintainable.
- It is energy effective.
- It has fully utilized the potential of daylight, when it is available.
Measurement of light – Light is measured in lumen and lux.
The amount of light given out by the light source is measured in lumen. But some of it gets lost, as mist, dirty fittings, coloured shades, dark coloured furnishings and distance absorb it. Hence the amount of usable light that reaches the work surface is often lesser than that which is emitted from the source. Lux is the measure of illumination at or on the surface being illuminated.
Glare – Glare is defined as dazzling brilliance which can obstruct vision. It can also produce eye damage and should be avoided. It can be caused by:
- Natural sunlight streaming in through the window.
- Reflected light from mirrors, shiny surfaces or even a white paper.
- Direct light from a naked bulb or spot-light.
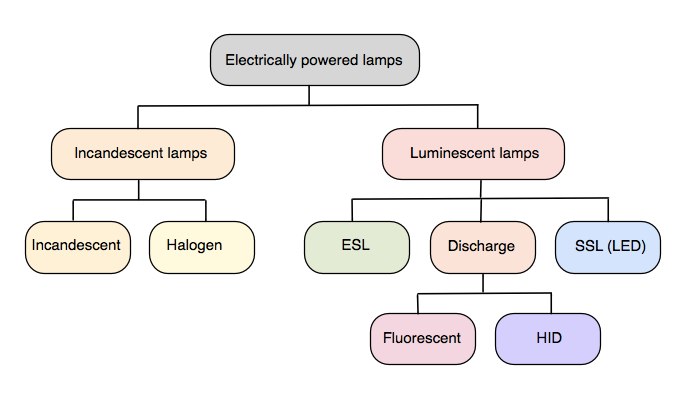
TYPE OF LIGHTING
SOURCE BASED CLASSIFICATION:-on the basis of source light can be classified as following.
- NATURAL LIGHT:-the bright day light is a major factor of designing hotel guestroom, especially where large wall area have been decorated with glass.
2 .ARTIFICAL LIGHT:-these are the man made light that helps us to see clearly and prevents accidents..They contribute to attractiveness of homes and hotel rooms. Artificial lights are of two type
- Incandescent/filament:-Here light is produced by heating a metal, generally, steel to that extent to which it glows. They have tungsten filament in a sealed container.
GLS (general lighting service) lamps which come in wide variety such as GLS clear, GLS argents and miniature lamps
- Fluorescent/discharge:-these are cold source of light. A glass tube with an inside coating of fluorescent is filled with vaporized mercury and argon and when electricity is passed through it, creating light. They come in vide range of colour. They consume less energy.
Depending upon the pressure present inside it they can be classified as follows
- Low pressure lamps:-these are most widely used tubular fluorescent lamp.vapuorised mercury is filled under low pressure
- High pressure lamps:-
HPMV: High pressure mercury vapour ,produces bluish, White light.
HPSV: High pressure sodium vapour produces golden, yellow Light.
CLASSIFICATIONS ON THE BASIS OF DIRECTION– Types of lighting are classified in the manner in which the light rays are directed to the object to be illuminated.
- Direct – When the light is directed straight from the source into the room, object or limited area, it is called direct lighting.
- Indirect lighting – This is where all the light is directed to a ceiling or a wall from which it is directed back into the room.
- Semi indirect lighting – Here some light is directed into the room, and some are allowed to be directing and reflecting from the ceiling.
- Diffused lighting – This is where the bulb or light source is completely enclosed and the light diffused through a translucent shade. Wall or ceiling panels can be used to conceal the light source.
CLASSIFICATION ON THE BASIS OF FUNCTION-
- GENERAL OR AREA LIGHTING:-This illuminates the whole room equally. This brings the design and colour of the room to uniform attention. This eliminates the bulkiness of the furniture, the darkness of shadow and harsh contrasts.
- .LOCAL OR SPECIFIC LIGHTING:-Local lighting can be provided by the lamps at strategic place. Fixtures attached on walls, under cabinet etc are grown in popularity. Chandeliers are the most popular form of local lighting.
This is of two types
- Task lighting
–reading or either close work
–sewing, needle work etc
–cooking, especially in area were knives are employed.
- Accent lighting
-highlighting a painting
-focusing on an architectural element
-breaking up a large room into an island
-visually enlarging a room
Methods of lighting – There are two basic methods:
- Architectural lighting
- Non-architectural lighting.
- Architectural lighting – This type of lighting provides functional lighting that is unobtrusive and good for contemporary rooms.
A).Track lighting – This can be fitted along the wall and ceiling.
B)Warning or safety lighting – All hazard areas such as steps, stairs, exits and fire escape routs should be well lit. Stairs can also be illuminated by a strip lighting processed in the handrail or by pendant lights
C)Valance lighting – A horizontal fluorescent tube is placed behind a valance board casting up light which reflects off the ceiling and then shines down the drapery, thus producing both direct (up light) and indirect (down light) light
D)Cornice lighting – A cornice is installed at the ceiling which directs the light downwards only. It gives dramatic effect on drapery, wall coverings and pictures.
E)Cove lighting – This consists of placing a continuous series of fluorescent tubes in a grave or trough placed on one or more walls of a room, about 12 inches from the ceiling. This enables the light to be thrown on the ceiling and then into the room
F)Soffit lighting – This refers to the underside panel of a built-in light source.
G)Luminous or recessed lighting – This is primarily used for kitchens, utility areas, bathrooms, etc.
2. Non-architectural lighting – This is the lighting that can be done after the construction of the building, by taking an electrical extension cord.
Ceiling and Wall fixtures
Portable lamps
LIGHT FIXTURES:-
- When buying lighting fixtures to implement a lighting scheme, theiras well as the light they produce should be satisfactory.
- Shades ,globes and even lamp base can look beautiful when illuminated
- Translucent shades produce distinct colour cast to their surrounding
- Opaque shades gives localized pool of light rather than all round illumination
- Material used for shades should not discolour with heat.
Different types of electrical lighting – The level of lighting is usually above the eye level. Whatever the source of light, the type of wall, floor, ceiling and colour affect the amount of effective luminance.
Concealed lighting – Filament bulbs or fluorescent tubes are concealed in the ceiling and diffused through opaque panels or elaborate screens of glass, crystal or parapex, metal leaves or pendant pieces.
Pendant ceiling lights – An electrical cord from the ceiling suspends the bulb. Bulb can be concealed in a large shade to avoid the glare. Pendant lights can be adjustable, so they can be raised or lowered over a desk or dining table.
Chandeliers – It is usually a group of low watt bulbs, suspended together. Light is reflected from crystal drops to avoid the glare.
Spotlights – Strategically placed in a room, they can be recessed into the wall or ceiling and/or, directed on to the wall or ceiling and reflected back to the room. It can be uncomfortable to someone sitting directly underneath it. It can be used to illuminate special features in the room.
Task lighting – This is a functional illumination provided by lights above working surfaces. Wall lights, desk and table lamps, standard and track lamps are examples of Portable lamps should be so positioned so that the base of the lamp is at eye level and should stand steadily with weighted base if necessary. Traveling flex is dangerous and untidy; and it can uncurl at the base and make the whole lamp unstable. Surplus flex should be looped and secured with rubber band or plastic loop. Adjustable task lights are more functional than ornamental ones.
Emergency lighting – This is required in all public buildings and is a requirement for fire certificate. It is necessary in all hazard areas including areas like lavatory and in homes for elderly and children.
Exterior lighting – For safety, security and advertising, it is necessary to have the exterior of the building or the building grounds illuminated. These lights should have waterproof casing and special bulbs.
General lighting – Light that shines unhindered in all directions from the source is referred to as general lighting. This can be mean bare tungsten or fluorescent bulb or one with a diffuser shade or translucent covering.
Factors to consider while planning a lighting system –
- Decide on the amount of light needed for an area.
- If artificial lighting is used, check the heat gain.
- It should be going with the décor and design of the area, and should be durable.
- There should be ease of replacement, especially if glass shades are used.
- The cleaning process should be simple and easy. It has been estimated that as much as 50% of the illumination can be lost if lamps and reflectors are not cleaned regularly.
- Cost of the lighting.
- If the illumination is enough for the work surface.
- The lighting scheme should allow for reflection and absorption of light and glare. Glare and reflected glare should be avoided, as it is bad for eyesight. It increases eyestrain and produces harsh lighted areas for working.
General requirement of lighting in a guest room is –
- Bed head light for reading in bed. An adjustable swivel jointed fitting with an incandescent bulb is most suitable.
- Decorative general lighting in room, with either chandelier or wall brackets using incandescent lighting.
- Indirect valance or cornice lighting
- Decorative standard floor lamps in corners or near seating area with bowl reflector lamps.
- Wall paintings and headings accentuated with directional lamps.
- Night lamp for direction during night.
- Lighting in bathroom should be both general and local. General lighting should be diffused but strong enough to penetrate the shower curtains. Depending on the size of the bathroom, additional local lighting may be required at the mirror for shaving and make-up purposes.
Uses of lighting in interior decoration –
- To reveal features of construction.
- Conceal space by leaving areas in shadows.
- Create impression of space. Using multi-light fittings give added perspective and feeling of space.
- Create suitable atmosphere for a room or an area.
- Act as a focal point.
- Accentuate and dramatize colour and texture.
- Highlight pictures, object d’arts, potted plants, flower arrangements, etc.
- Introduce accent of colour by fittings and shades.
- Lighted walls give a background to furnishings.
LIGHTING PLANS
- ENTRANCE AND LOBBY:
The entrance of any establishment should be inviting and light should be in its character and atmosphere of the place. In large area a chandelier, cove lighting, wall bracket etc can be used. A false ceiling with mirror can illuminate more light and can give the impression of great height, as well as providing interesting reflection of light.
- RESTAURANTS AND OTHER PUBLIC AREAS:
- The atmosphere in the longue should be of comfort and restfulness
- In cafeterias and coffee shop high degree of illumination is preferred in order to encourage high degree of turnover.
- Chandeliers may look elegant in a banquet hall
- GUESTROOM AND COORRIDOR:
- Guest should be able to see room number clearly, light fitting in corridor should not be fitted less than1.5 times their distance from the floor.
- Stairs should be well lit to avoid accidents. Light can be fitted into stairs themselves or just below the hand rail.
- Guestrooms do not necessarily require general lighting bit different parts of the room should be well lit. Switches should be easily accessible, especially near the entrance.
- Dressing table lamp should lit the face of the person standing before it.
- For reading and writing there should be ample light, which is adjustable.

