PLANNING
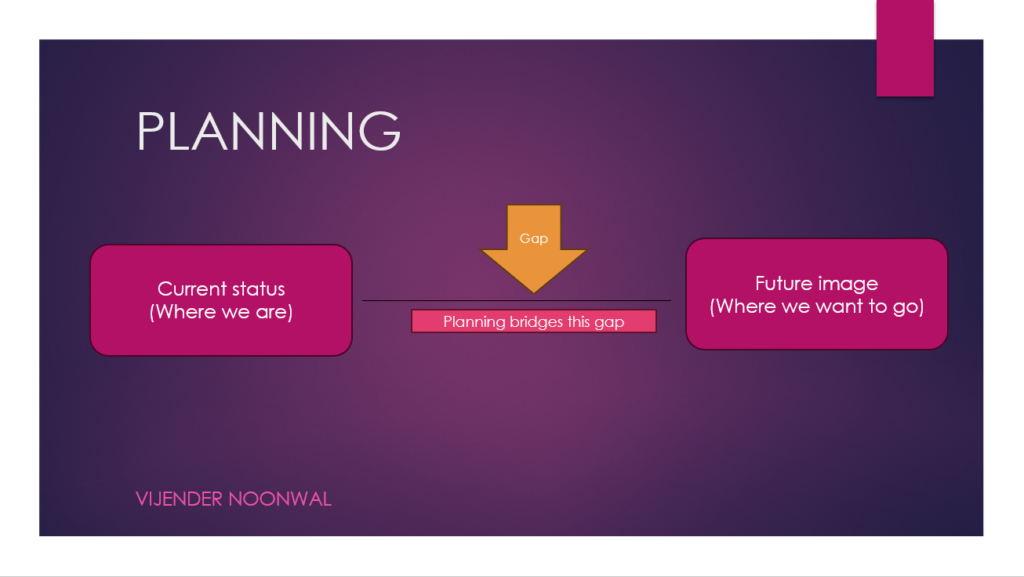
Planning is the beginning of the management process. “It is a process of ‘thinking before doing”.
“Dreams can be turned into reality only if business managers think in advance on what to do and how to do it. This is the essence of planning.”
MEANING
- Planning is deciding in the present, what is to be done in the future.
- Choice making
- Involves setting up of objectives
- Plans are always developed for a given time frame.
FEATURES OF PLANNING
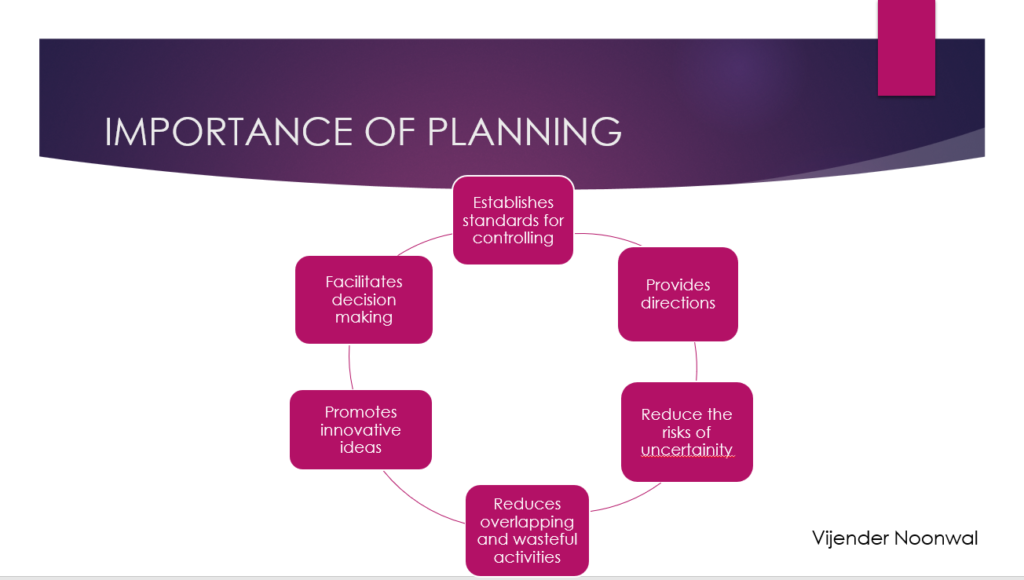
- Planning focuses on achieving objectives.
A. Objectives provide the basic guidelines for planning activities.
B. Planning has no meaning unless it positively contributes for achievement of predetermined goals
2. Planning is a primary function of management:
A. By setting up objectives in advance, planning directs all other managerial functions towards their attainment.
3. Planning is pervasive:
A. Top management undertakes strategic planning and middle and lower management are involved in departmental planning and operational planning, respectively
4. Planning is continuous:
A. Continuity of planning is related with planning cycle.
B. It means that a plan is framed, it is implemented and is followed by another plan and so on.
5. Planning is Futuristics:
A. “Planning involves thinking about the future for doing actions in the present”.
B. A business firm prepares its annual plan for production and sales based on sales forecasting.
6. Planning involves decision-making
7. Mental exercise
LIMITATIONS OF PLANNING
- Planning leads to rigidity
- Planning may not work in a dynamic environment
- Planning reduces creativity
- Planning involves huge costs
- Planning is a time-consuming process
- Planning does not guarantee success
EXTERNAL LIMITATIONS FOR PLANNING
- Natural calamities
- Changes in Government policies
- Strategies of competitors
- Technological changes
- Changes in fashion, taste, etc.
TYPES OF PLAN
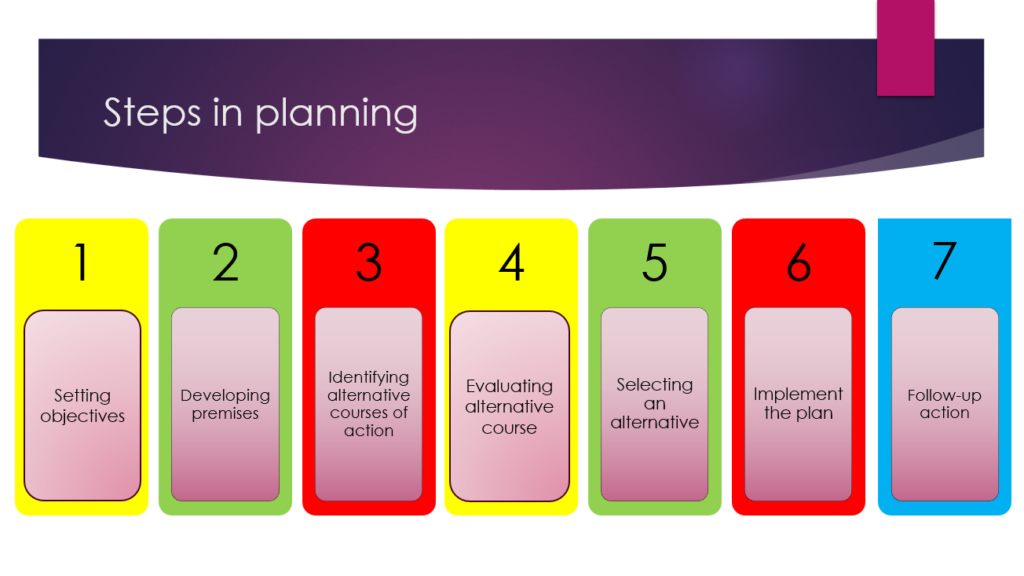
Plan is a document showing a detailed scheme, program, and strategy, worked out in advance for fulfilling an objective.
- Standing plans: is one which is used again and again, whenever particular situation arises like objectives, strategy and policy etc.
- Single-use plans: is one-time plan which is specifically designed to achieve a particular goal like budget.


