It is important to know how the animals are slaughtered in hygienic conditions. Meat bought must be from a slaughter house that has professional working.
In Europe, slaughter houses are called abbatoirs. The slaughter houses have space for meat storage and deal with large amounts of offals. A slaughter house is functional, compact in space, has satisfactory working conditions, proper equipment and has provision for the highest sanitary standards.
The different types of meat are: Lamb, Mutton, Beef, Veal, Pork and Game meat.
PRE-SLAUGHTER STEPS:
INSPECTION: animals are inspected by medical inspectors to assess whether the animals are fit for human consumption, then only, they are deemed fit for slaughtering.
RESTING OF ANIMAL: the animals are kept in clean dry enclosures (pens) to rest for 24 hours. The animals are given plenty of water during resting.
- It helps to maintain normal heartbeat of the animals
- It helps in the drainage of blood.
- It helps to have normal body temperature as it increases the keeping quality of the carcass and minimize the bacterial growth.
- It speeds up the glycogen stored in the muscle to turn to lactic acid, which will lower the pH of the muscles and reduce the growth of bacteria and act as a natural preservative.
- It shortens the rigor mortis (ripening or ageing) period (the carcass is hung in cool temperature during the period, the muscles become stiff. Certain enzymes/acids are produced that soften the meat).
FASTING: animals are fasted for at least 8 to 12 hours.
- It helps to reduce the amount of undigested food and clean the intestinal tract
- Bacterial infection will be minimized
- It improves the quality of the meat
- The blood left in the tissues will thus be free from absorbed nutrients.
WASHING: after resting and fasting, the animals are passed through a tunnel containing showers from top and bottom with lukewarm water and the animal is kept on a sliding platform and is washed from all sides and superficial dirt is removed.
STUNNING: it is to render the animal unconscious so that it may bleed freely and it may easily be killed. It is also done to avoid pain to the animal, while it is being killed.
Various ways of stunning:
- Knocking: the animal is hit with a heavy hammer (4lbs) on the head to make it unconscious. Not a very popular method in current scenario.
- Carbon dioxide chamber: the animals are made unconscious by putting them in these chambers, but not popular as the weak animals may die.
- Cartridge pistols/captive bolts: this is done by damaging the brain by placing the pistol between the eyes, this renders the animal unconscious.
- Electric tongs: this is the most popular method. The ends of tongs are placed behind the ears and a current (60-70 volts) is passed. This renders the animal unconscious for about 15-20 minutes.
STICKING: This is done with a knife, 6 inches long blade. It is done very soon after stunning when the heartbeat rate and blood pressure of animal is high. This helps to bleed freely. In India, there are two processes: HALAL: Muslims and some of the other communities prefer this meat, throat is quickly cut with a sharp knife with short strokes and bled). JHATKA: the head is severed from the body by a single blow from a long, heavy, butcher’s knife.
BLEEDING: The animals are hung on hooks with their heads downwards, as neither the animal nor the slaughterer comes into contact with the blood. Drains for the blood lead outside the building, either to a blood collecting tank or to a processing room.
FLAYING AND CLEANING: in this step, the air is blown between the flesh and skin to create space and the skin is pulled off. The stomach and intestines are removed, inspected and sent to the tripery section. Offals are removed and sent to the offal section. Now the carcass is ready to dissection.
FACTORS THAT GIVE MEAT A GOOD QUALITY:
- FAT
- COLOR OF THE MEAT
- TENDERNESS
FAT:
Fat in animal is found around the muscle fibers or between muscle fibers. It is interspersed between the muscle fibers. The fat seen as small flecks of fat within the muscle is known as marbling and enhances the flavor of meat. Fat contributes moistness to the meat, makes it tender, enhances flavor. It must has a pleasant smell.
COLOR OF THE MEAT:
The young animals have a lighter colored meat with a firm, dry, creamy white fat whereas the older animals have darker colored meat and a yellowish fat.
TENDERNESS:
The tenderness depends upon the food, the animal is fed on. The finer the grains, the more tender the meat. The amount of connective tissue is directly related to the tenderness of meat.
FACTORS THAT MAKES MEAT TENDER
- MOIST HEAT
- TENDERIZERS
- RIPENING OR AGEING OF MEAT
- MARINADING
- MECHANICAL POUNDING AND GRINING
APPROXIMATE ROASTING TIME FOR MEAT
BEEF: 15 to 20 minutes per 455 gms and 20 mins over
MUTTON: 25 mins. Per 455 gms and 20 mins.over
LAMB: 20 mins. Per 455 gms and 20 mins.over
VEAL: 25 mins. Per 455 gms and 20 mins.over
PORK: 25 mins. Per 455 gms and 25 mins.over
INTERNAL TEMPERATURE RECOMMENDED FOR ROASTING MEAT
BEEF | MUTTON |
RARE 60 DEG. C (140 DEG. F) | 60 DEG. C (140 DEG. F) |
MEDIUM 71 DEG. C (160 DEG. F) | 71 DEG. C (160 DEG. F) |
WELL DONE 82 – 85 DEG. C (180 -185 DEG. F) | 82 – 85 DEG. C (180 -185 DEG. F) |
ALL PORK MEAT IS WELL DONE | |
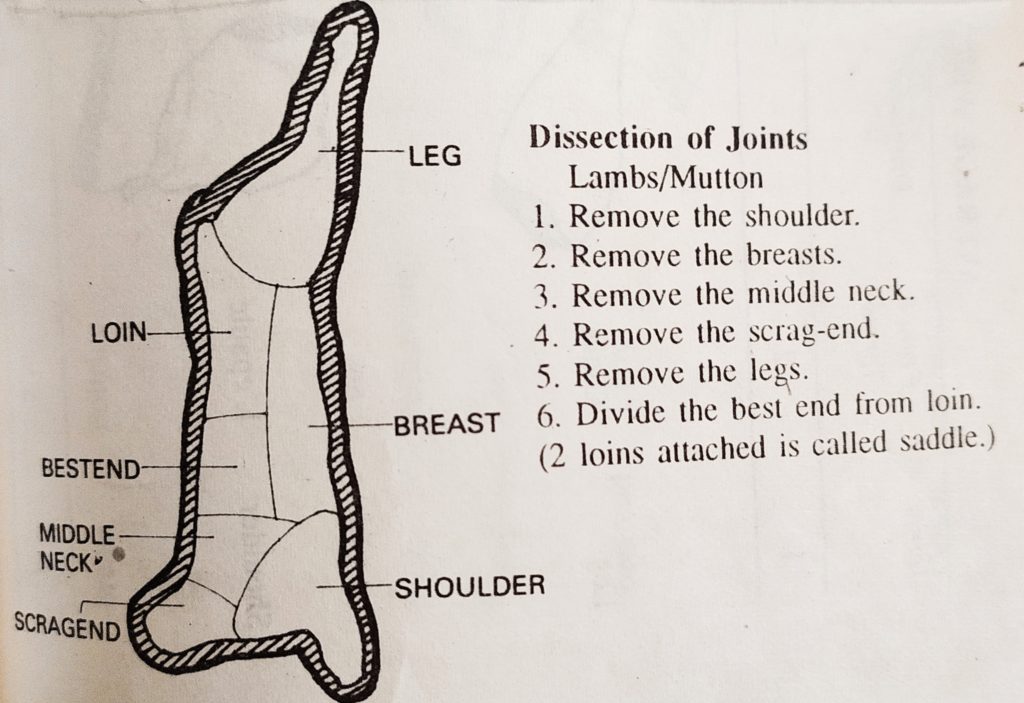
CUTS OF LAMB/MUTTON
LAMB is the meat of a young sheep, mutton the flesh of the mature sheep or goat. Lamb usually is the flesh of animals not more than 12 months of age. The average weight of an imported lamb is 16 kg, and for mutton, it is 25 kg. The average weight of Indian lamb is 10 kg to 14 kg and for mutton 20 kg to 22 kg.
CUTS OF PORK
The flesh of pig is called pork. Most of the pork meat comes from animals not more than a year old. It generally has more fat than other meats. A suckling pig is about 5 to 6 weeks old. The best quality joints of pig are the leg and loin of pork.
HAM:
It is taken from the hind leg of the pig. Preserved by curing or pickling in brine, then dried and smoked. Ham is prepared from fresh pork meat.
GAMMON:
It is taken from the leg of the pig that has been reared for bacon and the meat is cured. These are mild and do not keep as long as true hams.
BACON:
Bacon is obtained from the sides and back of a baconer (a pig reared and specially fed to yield bacon). It is cured with brine, once it is matured, it is sold as green bacon
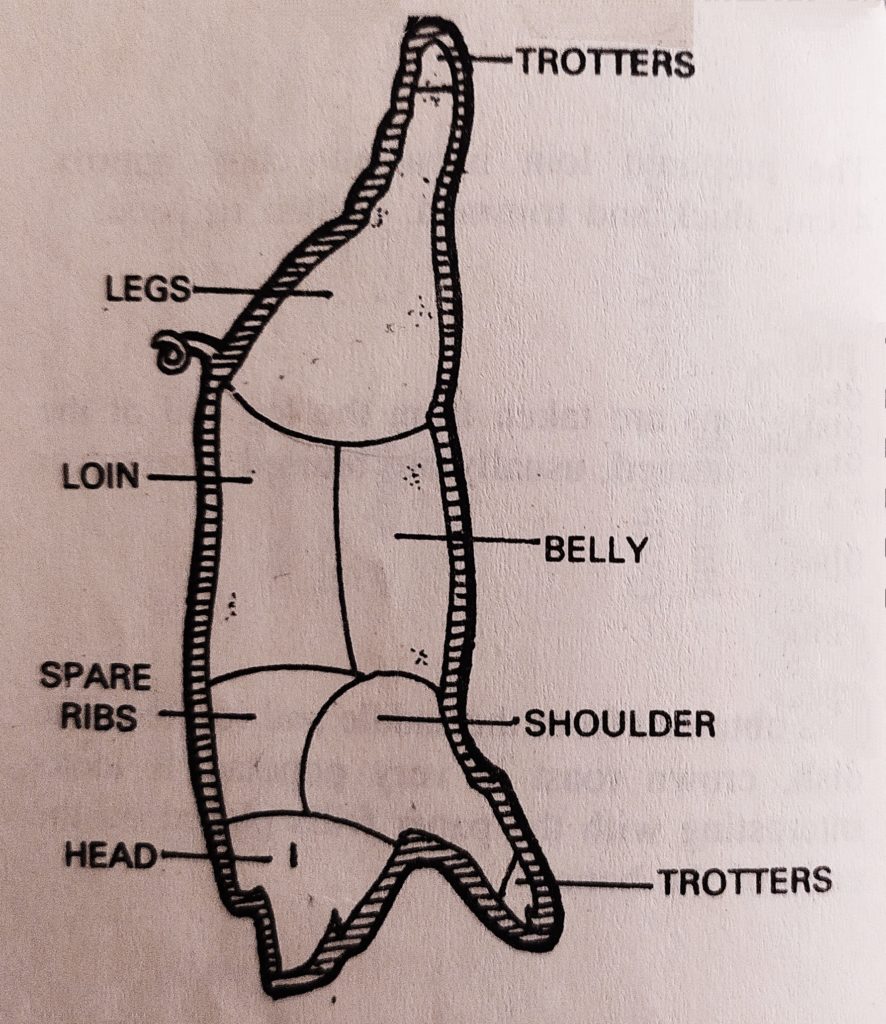
DISSECTION :
REMOVE THE HEAD
REMOVE THE TROTTERS
REMOVE THE LEGS
REMOVE THE SHOULDER
REMOVE THE SPARE RIBS
DIVIDE THE LOIN FROM THE BELLY
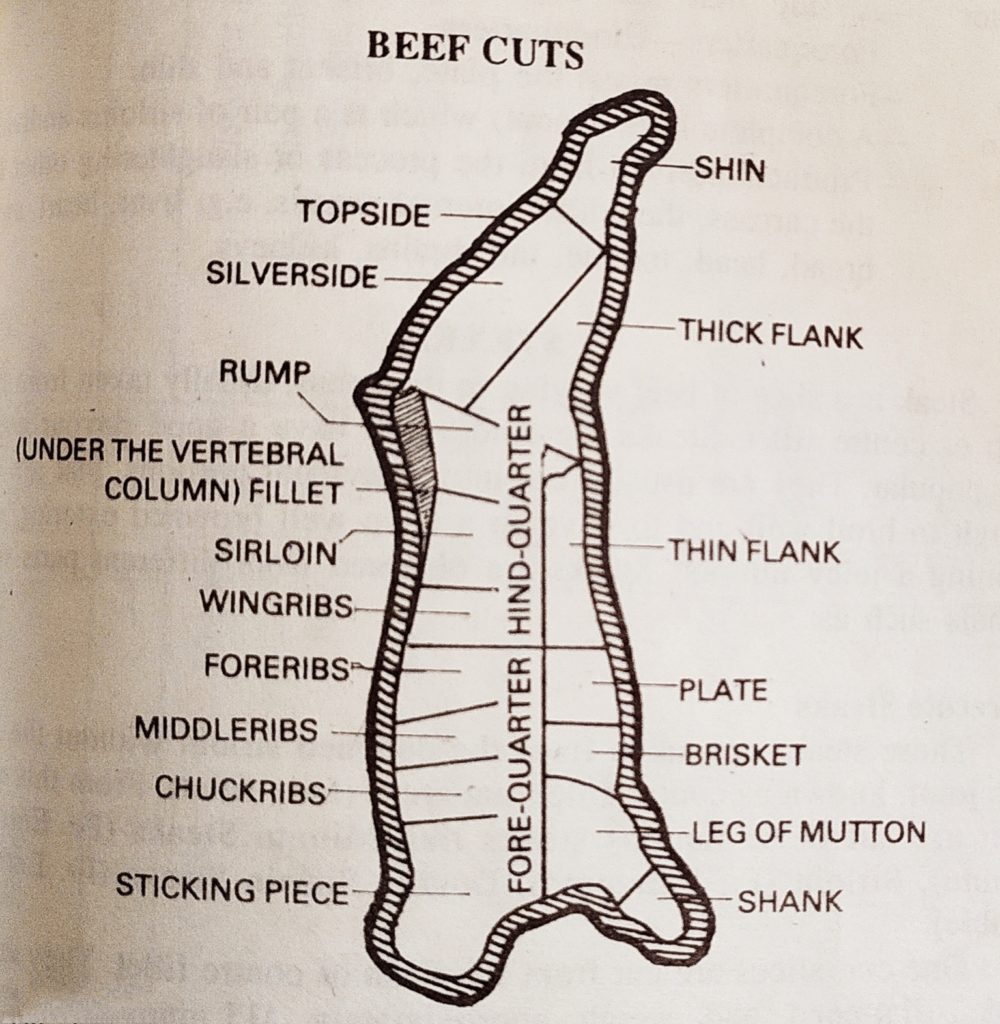
CUTS OF BEEF:
Veal: flesh of calf (less than three months of age) which lives on milk.
Calves: the animals are from 3 to 8 months
Beef: the meat is taken when the animal is above 8 months.
Beef is the most popular of all the edible meats in the western countries. In India, beef is not very popular and buffaloes are slaughtered in some places and sold as beef.
Beef is the flesh of steers, heifers, cows, bulls and stags. The age and the sex has an influence on the taste and quality of meat.
The carcass is divided into two sections:
Forequarter
Hindquarter
DISSECTION FOR HINDQUARTER:
THE WHOLE SIDE IS DIVIDED BETWEEN THE WING RIBS AND THE FORERIBS
REMOVE THE RUMP SUET AND KIDNEY
DIVIDE THE LOIN AND RUMP FROM THE LEG (TOPSIDE, SILVERSIDE, THICK FLANK AND SHIN)
REMOVE THE FILLET
DIVIDE THE RUMP FROM THE SIRLOIN
REMOVE THE WING RIBS
REMOVE THE SHIN
BONE OUT THE AITCH BONE
DIVIDE THE LEG INTO THREE REMAINING JOINTS (SILVERSIDE, TOPSIDE AND THICK FLANK)
DISSECTION FOR FOREQUARTER:
REMOVE THE SHANK
DIVIDE IN HALF DOWN THE CENTER
TAKE OFF THE FORERIBS
DIVIDE INTO JOINTS